Benutzer:Mauz/Isooberfläche
Eine Isooberfläche (isosurface) ist eine Fläche im Raum, deren Punkte alle einen konstanten Wert innerhalb eines Wertebereichs aufweisen (z.B. Druck, Temperatur, Geschwindigkeit, Dichte). Die Darstellung erfordert meist eine aufwändige Bildverarbeitung.
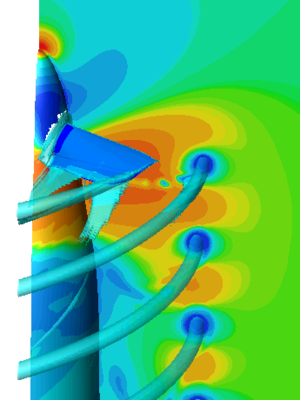
Visualizing isosurfaces is essential in many different fields of scientific research like Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), finite element modeling and medical and seismic tomography. These applications often use large unstructured grids made of millions of tetrahedra. Handling these kind of very large grids without out-of-core or parallel algorithms using a simple pc leads our approach. [1]
Anwendungen
speziell im Medizinischen Bereich. werden normalerweise mit Mitteln computer graphics, and are used as data visualization methods in computational fluid dynamics (CFD), allowing engineers to study features of a fluid flow (gas or liquid) around objects, such as aircraft wings. An isosurface may represent an individual shock wave in supersonic flight, or several isosurfaces may be generated showing a sequence of pressure values in the air flowing around a wing. Isosurfaces tend to be a popular form of visualization for volume datasets since they can be rendered by a simple polygonal model, which can be drawn on the screen very quickly.
In der medizinischen Bildverarbeitung werden Isooberflächen zur Darstellung von Knochen, inneren Organen oder speziellen Strukturen verwendet, speziell bei der dredimensionalen Computer-Tomografie.
Numerous other disciplines that are interested in three-dimensional data often use isosurfaces to obtain information about pharmacology, chemistry, geophysics and meteorology.
Bildverarbeitung
A popular method of constructing an isosurface from a data volume is the marching cubes algorithm, and another, very similar method is the marching tetrahedrons algorithm.
Examples of isosurfaces are 'Metaballs' or 'blobby objects' used in 3D visualisation. A more general way to construct an isosurface is to use the function representation and the HyperFun language.
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ Luc Buatois, http://hal.inria.fr/docs/00/10/55/84/PDF/ISVC06_BuatoisEtAl.pdf GPU Accelerated Isosurface Extraction on Tetrahedral Grids
See also
External links
[[Category:3D Bildverarbeitung]] [[Category:Medizinische Bildverarbeitung]] [[Category:Oberflächen]]