2MASS J11101001+0116130
aus Wikipedia, der freien Enzyklopädie
Dies ist die aktuelle Version dieser Seite, zuletzt bearbeitet am 28. Mai 2020 um 05:32 Uhr durch imported>Crazy1880(385814) (tk k).
| Brauner Zwerg 2MASS J11101001+0116130 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beobachtungsdaten Äquinoktium: J2000.0, Epoche: J2000.0 | |||||
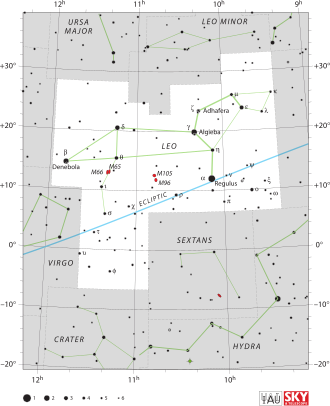
| Sternbild | Löwe | ||||
| Rektaszension | 11h 10m 10,01s[1] | ||||
| Deklination | +01° 16′ 13,1″[1] | ||||
| Scheinbare Helligkeit | J-Band: 16,12 mag[2] | ||||
| Parallaxe | 52,1 mas[3] | ||||
| Typisierung | |||||
| Spektralklasse | T5,5[4] | ||||
| Physikalische Eigenschaften | |||||
| Andere Bezeichnungen und Katalogeinträge | |||||
| |||||
2MASS J11101001+0116130[1], auch als SDSS J111010+011613 (kurz SDSS 1110) bezeichnet, ist ein Brauner Zwerg der Spektralklasse T5,5[4] im Sternbild Löwe. Seine Position verschiebt sich aufgrund seiner Eigenbewegung jährlich um 0,3403 Bogensekunden.[3][5] Er wurde 2002 von Thomas R. Geballe et al. entdeckt.[6]
Weblinks
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b M. F. Skrutskie, R. M. Cutri, R. Stiening, M. D. Weinberg, S. Schneider: The Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS). In: The Astronomical Journal. Band 131, Nr. 2, 2006, ISSN 0004-6256, S. 1163–1183, doi:10.1086/498708 (iop.org [abgerufen am 4. Mai 2019]).
- ↑ C. G. Tinney, Jacqueline K. Faherty, J. Davy Kirkpatrick, Mike Cushing, Caroline V. Morley: THE LUMINOSITIES OF THE COLDEST BROWN DWARFS. In: The Astrophysical Journal. Band 796, Nr. 1, 4. November 2014, ISSN 1538-4357, S. 39, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/796/1/39 (iop.org [abgerufen am 4. Mai 2019]).
- ↑ a b Trent J. Dupuy, Michael C. Liu: THE HAWAII INFRARED PARALLAX PROGRAM. I. ULTRACOOL BINARIES AND THE L/T TRANSITION ,. In: The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. Band 201, Nr. 2, 1. August 2012, ISSN 0067-0049, S. 19, doi:10.1088/0067-0049/201/2/19 (iop.org [abgerufen am 4. Mai 2019]).
- ↑ a b Adam J. Burgasser, T. R. Geballe, S. K. Leggett, J. Davy Kirkpatrick, David A. Golimowski: A Unified Near‐Infrared Spectral Classification Scheme for T Dwarfs. In: The Astrophysical Journal. Band 637, Nr. 2, 2006, ISSN 0004-637X, S. 1067–1093, doi:10.1086/498563 (iop.org).
- ↑ R. F. Jameson, S. L. Casewell, N. P. Bannister, N. Lodieu, K. Keresztes: Proper motions of field L and T dwarfs. In: Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. Band 384, Nr. 4, 2008, ISSN 0035-8711, S. 1399–1413, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12637.x.
- ↑ T. R. Geballe, G. R. Knapp, S. K. Leggett, X. Fan, D. A. Golimowski: Toward Spectral Classification of L and T Dwarfs: Infrared and Optical Spectroscopy and Analysis. In: The Astrophysical Journal. Band 564, Nr. 1, 2002, ISSN 0004-637X, S. 466–481, doi:10.1086/324078.